4 known side effects of antidepressants

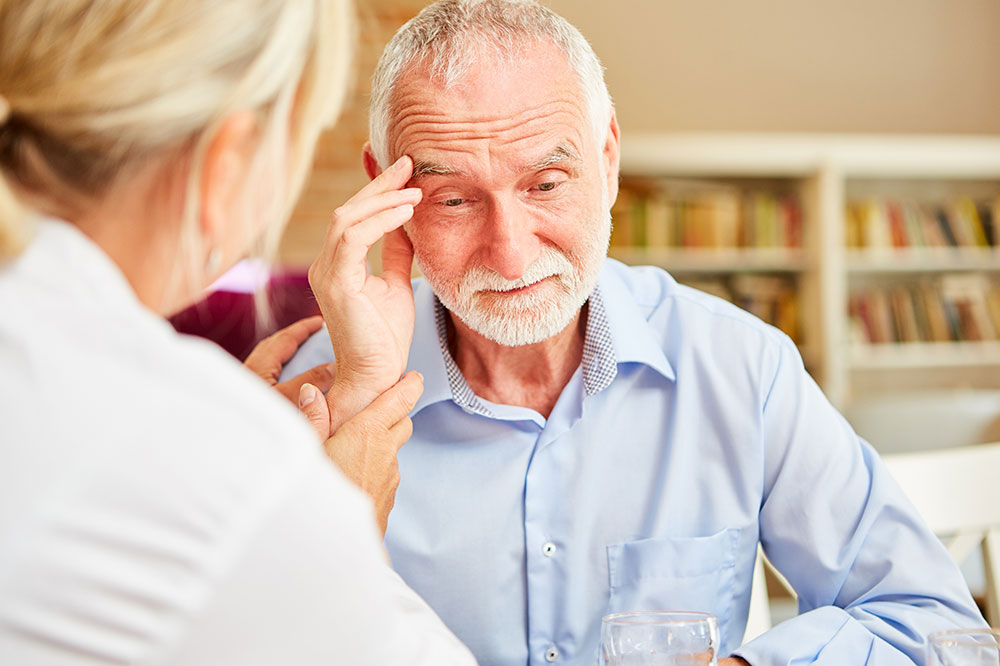
Typically intended for the management of mental health conditions like depression and anxiety, antidepressants can help relieve symptoms of these disorders. However, it is important to know exactly what to expect when one is prescribed this form of treatment. Given how powerful they are, antidepressants come with a few side effects—both minor and major. Here is a look at some of the common side effects to help one make an informed decision:
1. Drop in sodium levels
Some antidepressants can trigger a severe drop in sodium levels in the blood, which is also called hyponatremia. This side effect is often more common among older adults, as fluid and sodium regulation becomes more difficult with age. The low sodium levels tend to cause a build-up of fluids inside the cells, an outcome that can lead to complications like headaches, muscle pain, a reduced appetite, sickness, confusion, agitation, psychosis, seizures, disorientation, and feeling tired and listless without engaging in any physical activity. Certain antidepressants tend to suppress the hormones that regulate sodium and fluid levels.
2. Diabetes
Certain studies have found a link between long-term antidepressant usage and diabetes. According to the research, those on antidepressants are at a higher risk of developing type-2 diabetes than those who are not. Nevertheless, one should not worry too much about this connection, as the direct association between antidepressants and diabetes is yet to be established beyond reasonable doubt. Even so, taking antidepressants in moderation (or as much as any general physician or other healthcare expert has prescribed for usage) is necessary.
3. Signs of hypomania
Signs of hypomania are a possible side effect of antidepressants. As antidepressants try to change the chemical balance in the brain, one may experience periods of over-active and high-energy behavior. This is not common for all antidepressants. So, if one notices such signs, they may talk to their healthcare professional to see if the prescription needs to be modified to account for this side effect.
4. Antidepressant discontinuation syndrome
Those who are on antidepressants for a long period and then stop cold turkey are likely to develop this syndrome. With this, they may notice issues like insomnia, nausea, dizziness, lightheadedness, sensory issues like tingling, burning or shock-like sensations, anxiety, agitation, irritability, and flu-like symptoms such as achiness, sweating, fatigue, and headache. While these symptoms will not be overtly severe, they are unpleasant and can last for one to two weeks.
Some other less common side effects of antidepressants are bleeding and blood loss. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) is an adverse reaction to certain antidepressants; however, this is a rare complication. Nevertheless, t o avoid unnecessary surprises with any type of treatment, one should discuss the risks and benefits of all suitable options with their doctor.