7 foods that may trigger eosinophilic esophagitis

Eosinophilic esophagitis is a condition wherein the esophagus gets inflamed, leading to difficulty in swallowing food, chest pain, and acid regurgitation. One type of eosinophilic esophagitis is reflux esophagitis, which often worsens inflammation. Moreover, the subtype is a complication that may stem from acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Apart from treatments and other remedies, avoiding certain foods may prevent acid reflux, reducing the risk of inflammation in the esophagus.
Foods that can trigger eosinophilic esophagitis or reflux esophagitis
Tomatoes
Tomatoes or their by-products are rich in malic and citric acid. These ingredients can trigger excess production of gastric acids in the stomach. So if an individual has too many tomatoes, it may create enough gastric acid to force the food back up to the esophagus and may lead to GERD, a contributing factor to reflux esophagitis.
Onions
Eating onions is often associated with increased production of gastric acid. The food takes longer to digest and thus might lead to bleaching, a common symptom of GERD. Furthermore, while people who cook onions may notice improvements in some symptoms of acid reflux, the food may still produce more acid. Therefore, to avoid any complications in the esophagus, one should reduce the consumption of onions or turn to green onions instead.
Sodas
Drinking sodas once in a while may not worsen symptoms of eosinophilic esophagitis. Still, one is better off avoiding such carbonated drinks because the gas bubbles add to gastric pressure. The phenomenon stretches the stomach and forces the esophageal sphincter to open. Moreover, the caffeine present in some sodas may also trigger acid reflux due to its acidic nature.
Soy sauce
Soy-based foods like soy sauce may also be unhealthy because of its acidic nature, with a pH value of about four or five. Soy-based foods such as tofu, edamame, and miso can worsen symptoms in people with eosinophilic esophagitis.
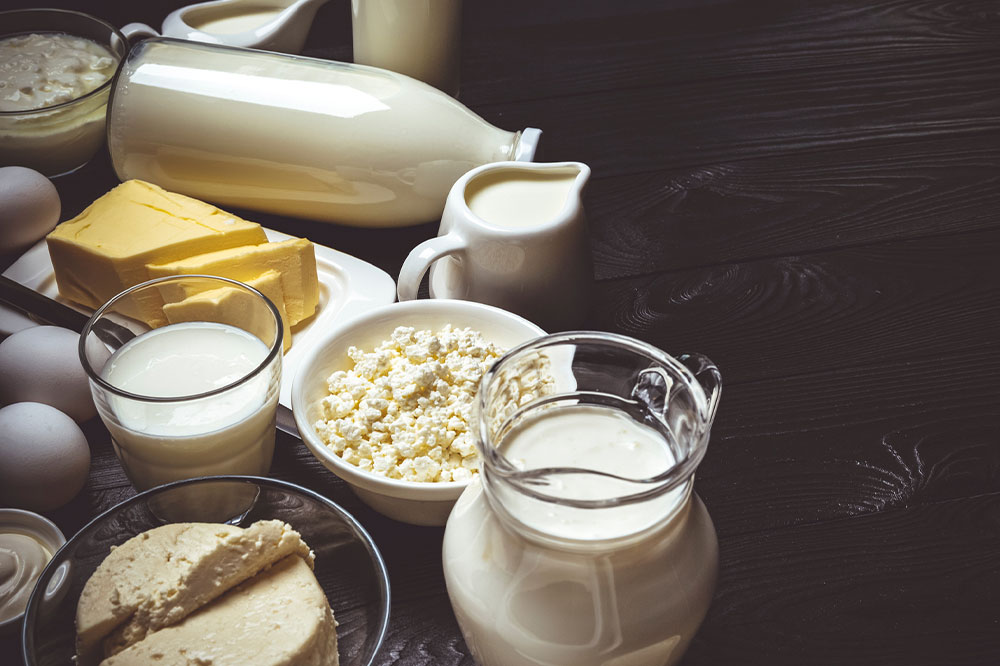
Milk
Milk and other dairy products like cheese can worsen the symptoms of GERD. These foods are high in fats that can lead to gastric acid production and push liquid or solid-based dairy products back to the esophagus. The process will ultimately worsen the symptoms of eosinophilic esophagitis.
Chili peppers
Chili peppers fall under a wide range of spices that can add flavor to an individual’s meals. The flavor comes from a flavoring agent in the food known as capsaicin, which also triggers a burning sensation in the mucous membranes in the digestive tract. Furthermore, the burn increases stomach acid production, which aggravates symptoms of eosinophilic esophagitis.
French fries
Fried foods like french fries are unhealthy in several ways for the human body, especially so for individuals with eosinophilic esophagitis. The fries are rich in saturated fats and require the stomach to produce more acid to digest them. The food can also take longer to break down. Therefore, the consumption of these fried foods can lead to reflux esophagitis.